
Dimdima
Online Children's Magazine from India

Dimdima
Online Children's Magazine from India
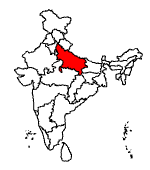
Uttar Pradesh, or UP is India’s most populous state. Areawise, it comes fourth.
Area: 2,38,566 sq km
Population : 16,60,52,859.
Language : Hindi and Urdu
Capital : Lucknow
Literacy rate : Female literacy is low: only 26 per cent can read and write among males
Physiography :
The state has three distinct physical divisions: the Himalayas in the north; the Gangetic plain in the middle and the Vindhya hills and plateau in the south.
The Himalayan region is characterised by snow-covered peaks, deep canyons and roaring streams that give rise to some of India’s major rivers including the Ganga, Yamuna, Ghagra and the Gomti. The mountains rise to more than 7000 m in places and include several prominent peaks such as Nanda Devi, Kismet and Badrinath. South of the Himalayas are the Siwaliks within which are located many of north India’s popular hill resorts, including Mussoorie, Nainital and Ranikhet.
Along the southern fringes of the Siwaliks is the Terai, a swampy lowland belt reputed to be one of the most unhealthy regions of India. Formerly it was covered with thick forests and tall grasses but now deforestation has denuded the land. The Gangetic plain covers about three-fourths of UP. The Ganga which flows through a greater part of the state, is the physical and spiritual life source of the region. The southern boundary of the state encompasses the plateau area of the Vindhyas.
Often referred to as the ‘cow belt’ or ‘Hindi belt’, Uttar Pradesh has been the most dominant state in Indian politics and culture since independence, producing eight of India’s prime ministers.
Many of the mahajanapadas (great states) of
ancient India flourished in the region now known as Uttar Pradesh. Gautama Buddha travelled extensively in this region; he preached his first sermon at Sarnath near Varanasi.
Uttar Pradesh came under the rule of various dynasties down the centuries, including the Mauryas, the Kushanas and the Guptas.Mathura emerged as the centre of power when the Kushanas under Kanishka made it their capital. Kanauj came into prominence when Harshvardhana made it his capital.
In the 12th century, Muhammad Ghori defeated Raja Jaichand of Kanauj.Thereafter, whoever ruled Delhi ruled Uttar Pradesh. Agra became the centre of power under the Mughals. Akbar the Great built his new capital city, Fatephur Sikri, near Agra. His grandson, Shahjahan, built the famous Taj Mahal in Agra on the banks of the Yamuna.
Uttar Pradesh became the meeting ground of two great religions — Hinduism and Islam. Kabir and his mentor Swami Ramananda upheld the essential values common to all religions.
After the disintegration of the Mughal empire, Awadh emerged as the centre of power in this region. Following the annexation of Awadh, the British created the administrative unit called the United Provinces of Agra and Awadh.
Mangal Pandey who struck the first blow for freedom heralding the outbreak of the revolt of 1857 belonged to Ghazipur, southern UP. The revolt had its greatest impact in the United Provinces.
Though the revolt was ruthlessly suppressesd, the struggle for freedom was resumed at the beginning of the 20th century. Chandrashekar Azad the revolutionary and Ganesh Shankar Vidyarthi were from this region. Allahabad under the leadership of the Nehrus emerged as a citadel for Swaraj. When the country became independent, Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru took over as the Prime Minister. Uttar Pradesh has the distinction of providing the country with as many as eight prime ministers — Prime Minister Vajpayee was elected to the Lok Sabha from the Lucknow constituency.
The holy river Ganga flows through several towns of U.P. Haridwar or the ‘Gates of Heaven’, is where all pilgrimages to the mountain shrines traditionally begin. According to time-honoured custom, a pilgrim should visit these dhams geographically, from west to east - beginning with Yamunotri, then Gangotri, Kedarnath and finally Badrinath.
The sacred Sangam at Allahabad is the confluence of three holy rivers - Ganga, Yamuna and the mythical Saraswati. The Maha Kumbh Mela,India's largest religious fair, is held here every twelve years.
The region of the Brajbhoomi has several towns and hamlets still alive with the Krishna legend. Picturesque ghats and temples emphasize the sacred character of Mathura. Among the most important of Mathura’s 25 ghats is the Vishram Ghat, where as legend has it, Krishna took rest after killing the tyrant, Kamsa.
Varanasi,on the banks of the Ganga,is one of the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world and the country's holiest.
Agra, once the capital of the Mughals, is famous because of the Taj Mahal. Built over a period of 22 years, it is one of the wonders of the world.
Near Agra, at Fatehpur Sikri, is the capital built by Akbar. Jodhabai’s Palace, the largest of all the palaces here, an ornately carved palace ascribed to Birbal, the legendary wit in Akbar’s court and the Buland Darwaza, built after Akbar’s successful conquest of Gujarat, still stand today.
Lucknow, once the 'city of Nawabs' is famous for the Bara Imambara, built by Nawab Asaf-ud-Daula in 1784. Its central hall is the largest vaulted chamber in the world.
India's first national park, the Corbett National Park is in the foothills of the Himalayas in U.P. It was designated the first Project Tiger Reserve in 1973.
Mussoorie and Nainital are two of India’s most frequented hill stations. Most towns in the Kumaon and Garhwal areas of U.P. offer facilities for adventure sports, including white water rafting.
Dimdima is the Sanskrit word for ‘drumbeat’. In olden days, victory in battle was heralded by the beat of drums or any important news to be conveyed to the people used to be accompanied with drumbeats.
Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan
K. M Munshi Marg,
Chowpatty, Mumbai - 400 007
email : editor@dimdima.com
Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan
505, Sane Guruji Marg,
Tardeo, Mumbai - 400 034
email : promo@dimdima.com
Dimdima.com, the Children's Website of Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan launched in 2000 and came out with a Printed version of Dimdima Magazine in 2004. At present the Printed Version have more than 35,000 subscribers from India and Abroad.