
Dimdima
Online Children's Magazine from India

Dimdima
Online Children's Magazine from India
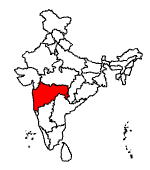
Maharashtra Maharashtra is the third largest state in area and population.
Area : 3,07,713 km
Population : 9,97,52,247
Capital : Mumbai, which was earlier known as Bombay is not only the state capital but also known as the business and trade capital of India.
Physiography :
The state can be broadly divided into 3 major parts: The Konkan, a coastal strip, about 720 km long and not more than 80 km wide; the Ghat region, also known as Sahyadris which runs almost parallel to the Konkan region; the Deccan, vast plateau to the east of the Sahyadris, comprising a major part of Maharashtra.
Major Towns & cities :
Pune (an educational and cultural centre), Sholapur (an industrial town), Kolhapur (known for sugarcane and gur), Nashik (a pilgrim centre), Nagpur (second capital) and Aurangabad (a historical town).
Major Rivers :
The Bhima, the Krishna and the Godavari are the major rivers and all of them flow eastwards. There are numerous rivers and rivulets which flow westwards in the Konkan region. These are mainly seasonal and shorter in length.
Crops :
The principal food crops are rice, wheat, jowar, bajra and pulses. The important cash crops are sugarcane, cotton and tobacco.
Maharashtra has had a long and varied history. The earliest empire to control the region was the Mauryan. Among the numerous dynasties that ruled over this area, in later centuries were the Satavahanas, the Vakatakas, the Chalukyas and the Rashtrakutas.
Huen Tsang mentions Pulakesin II of the Chalukyas as among the most powerful kings in the Maharashtra region.
This is the first mention of Maharashtra found in history.
Shivaji, the son of a feudatory chieftain, carved out the Maratha empire in 1674, during the reign of Aurangzeb, the Mughal. The Marathas became strong under the Peshwas. Originally advisors to Shivaji’s successors, they soon became defacto rulers. During the 1800s , a vast region comprising several parts of northern and eastern India came under Maratha control. The Afghans in the 3rd battle of Panipat shattered their power in 1761.
In several wars with the British, the power of the Marathas was further reduced. The Peshwas were compelled to accept defeat and retreated to Pune on a pension.
Under the British, the Bombay Presidency administered Western India. Montstuart Elphinstone governor of the Bombay Presidency in the 1820s established numerous educational and cultural institutes. The British played a role in making Maharashtra one of the most industrialized of the Indian states. Nagpur developed as an industrial centre after the completion of the Great Indian Peninsula Railway in 1867. This led to the introduction of the cotton crop and textile mills in the region.
In 1947, Bombay Presidency became Bombay state. The present boundaries of Maharashtra state were drawn in 1960 when Marathi-speaking areas, were separated from Gujarati-speaking areas of the huge bilingual state of Bombay, to form the two states of Maharashtra and Gujarat.
Maharashtra presents a fascinating mix of the old and the new.
The presence of the old is visible in the Elephanta caves and the Ajanta and Ellora caves built more than 1300 years ago. Coastal towns with beaches like Ganapati Phule and Guhaghar pepper the Konkan coast.
Bombay, now Mumbai, the state’s capital, has several monuments. At Bassein is an old Portuguese fort. The British erected many edifices including The Gateway of India, the Afghan Church and the University with the Rajabai clock tower. At Worli, lies the shrine of Haji Ali, a Sufi saint.
Mumbai is the single largest film producer in the world, with about 800 movies in 12 languages completed in its studios every year. Some of India’s most talented cricket players, including Sachin Tendulkar, honed their skills in Mumbai’s numerous playing grounds.
Pune, the capital of the Maratha kingdom under the Peshwas, is associated with some of the great names of India’s freedom struggle like Tilak and Gokhale.
Mahabaleshwar and Panchgani are hill stations, nearly 300 km from Mumbai.
Aurangabad, named after Aurangzeb has a tomb built by the Mughal emperor for his wife, the Bibi Ka Makbara. Daulatabad, near Aurangabad, has an impressive medieval fortress on a pyramid-shaped hill. Satara and Kolhapur are historical cities, where Shivaji’s descendants ruled for several decades in the 18th century.
Nasik on the Godavari is one of our holy cities. Some of the old temples built by the Chalukyas in the 11th century are found around here. Ahmednagar is famous for its fort, which served as a prison for prominent Indian leaders during the freedom struggle.
Maharashtra has its distinct festivals and traditions that are very popular. The Gokulashtami, the birthday of Krishna, is marked by the formation of human pyramids in every locality, attempting to reach the pot of curds hung at a great height. The Ganapati festival is observed in an ostentatious manner with huge idols of the deity being set up in various places. The idols are immersed in the sea after being carried in procession amidst great fanfare and revelry.
On Gudi Padwa, Maharashtrians celebrate their New Year. The delicacy called the ‘puranpoli’ a sweet made of gram flour and jaggery is specially prepared for the occasion.

Dimdima is the Sanskrit word for ‘drumbeat’. In olden days, victory in battle was heralded by the beat of drums or any important news to be conveyed to the people used to be accompanied with drumbeats.
Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan
K. M Munshi Marg,
Chowpatty, Mumbai - 400 007
email : editor@dimdima.com
Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan
505, Sane Guruji Marg,
Tardeo, Mumbai - 400 034
email : promo@dimdima.com
Dimdima.com, the Children's Website of Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan launched in 2000 and came out with a Printed version of Dimdima Magazine in 2004. At present the Printed Version have more than 35,000 subscribers from India and Abroad.